Do you fear losing your data? If yes, then you are not alone! A lot of businesses are struggling to safeguard their data from cyber-attacks.
Yes, cyberattacks have become more advanced while businesses are more vulnerable.
Regardless of your business type, it is virtually unavoidable to prevent your business from cyber-attackers. However, while around 81% of cyber-attacks happen to small & medium-sized firms, 97 percent of these attacks are avoidable by outsourcing cybersecurity solutions or by executing suggested security practices and elevating security recognition among employees. I’ll come to that part later.
But, here are some alarming statistics that give a decent idea of the cybersecurity arena as a whole.
- In 2019, the worldwide cybersecurity market size was evaluated at USD 156.5 billion. It is predicted to increase at a CAGR of 10.0 percent from 2020 to 2027.
- Data violations revealed 4.1 billion records at the beginning of 2019. (Source: RiskBased)
- As per Gartner, the global data security market is anticipated to touch $170.4 billion by 2022.
- 52% of breaches highlighted hacking, 28% covered malware, and 32–33% covered social engineering or phishing. (Source: Verizon)
- According to Cybint solutions, 62 percent of businesses encountered social engineering attacks and phishing in 2018.
- 71% of violations were economically inspired and 25% were inspired by espionage. (Source: Verizon)
- A report by Accenture states, 68 percent of business officers believe their cybersecurity dangers are growing.
- The predicted number of passwords utilized by humans and systems globally will increase to 300 billion by 2020. (Source: Cybersecurity Media)
If these statistics don’t sound alarming, then I have something more to tell you!
Highlights of Contents
Here a Few Biggest Cyber Attacks that Need Your Attention
1. Adobe
Date: October 2013
Impact: 153 Million User Records
What Happened?
In October 2013, Adobe reported that hackers had seized around 3M encrypted consumer credit card records along with the login information for an unknown number of accounts.
After a month, Adobe raised that assessment to incorporate IDs, as well as encrypted passwords for 38M “active users.” Krebs stated that a file posted days earlier “appears to include more than 150 million usernames and hashed password pairs taken from Adobe.” Research displayed that the hack had even revealed usernames, IDs, passwords, and credit & debit card information.
2. eBay
Date: May 2014
Impact: 145M Users
What happened?
eBay reported that an attack exposed its complete account list of 145M customers in May 2014, which includes dates of birth, name, addresses, and encrypted passwords. The organization said hackers utilized the credentials of three employees to access its network, as well as had entire access for around 229 days, which is more than sufficient time to compromise the customer database.
3. Canva
Date: May 2019
Impact: 137M User Accounts
What Happened?
In May 2019, an Australian graphic design software website, Canva, encountered an attack that revealed cities of residence, email addresses, names, usernames, and hashed and salted with bcrypt passwords. As per Canva, the hackers succeeded to see, but not a thief, files with biased payment data and credit cards.
4. Twitter
Date: July 2020
Impact: 130 Accounts Targeted
What Happened?
On the 15th of July, Twitter was attacked in a historic way. One-by-one, several accounts were aimed at and compromised, which include verified accounts of popular users, such as Bill Gates, Kanye West, Elon Musk, Joe Biden, and Barack Obama. Besides, multiple Twitter accounts for core cryptocurrency exchanges even begun posting texts as shown:
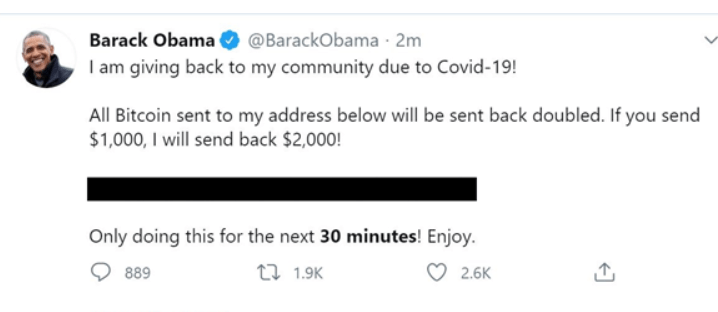
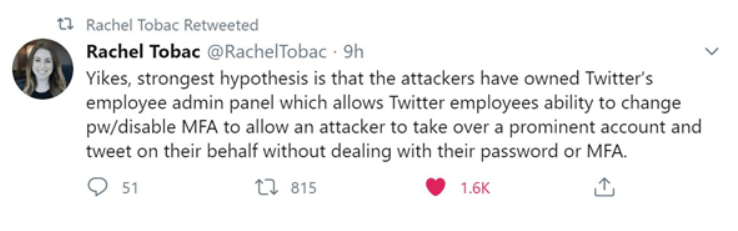
Twitter has consequently declared that 130 accounts were aimed – and of those merely 45 were breached. The first reasonable speculation on the purpose of the hack appeared from @RachelTobac:
As now you know how cybersecurity is turning into a huge problem for all of us, let’s move ahead and view different types of cybersecurity.
Different Types of Cybersecurity Attacks

“It takes 20 years to build a reputation and a few minutes of cyber-incident to ruin it.” ― Stephane Nappo
1. DoS and DDoS Attacks
A denial-of-service attack destroys the resources of a machine and does not allow it to reply to a service request. On the other hand, DDoS is an attack on the resources of the system, but it is released from several host systems that are affected by a malicious tool regulated by the attacker.
As compared to other attacks that are developed to facilitate the attacker to improve or gain access, DoS does not give direct advantages for attackers.
For a few of them, it is sufficient to have the fulfillment of service denial. Nevertheless, if the infected resource relates to a business contender, then the advantage to the intruder may be genuine enough.
The other goal of a DoS attack is to take a machine offline so that it can lead to a different attack. One prevalent instance is session hijacking.
Different types of DDoS and DoS attacks are smurf attack, TCP SYN flood attack, ping-of-death attack, teardrop attack, and botnets.
2. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attack

In a MitM, a hacker injects itself between the interactions of a server and a client. Here are a few general signs of MitM attacks:
- Session hijacking: In this type of cyberattack, an attacker seizes a session between a network server and a trusted client. The attacking machine changes its IP address for a reliable customer, whereas the server proceeds with the session, considering it is interacting with the client.
- IP Spoofing: A cyber attacker uses IP spoofing to influence a machine that it is interacting with a familiar, committed entity and give the attacker access to the device.
The cyber attacker transmits a package with the IP address of a recognized, reliable host rather than its own IP address to an objective host. The aim host may allow the packet and work upon it. - Replay: A replay attack happens when an intruder prevents and protects old texts and then attempts to transfer them later, representing one of the associates. It is simple to retaliate with session nonce or timestamps.
Recently, there is no one configuration or technology to avoid all MitM attacks. Usually, digital certificates and encryption give efficient protection against MitM attacks, guaranteeing both the integrity and confidentiality of interactions.
3. Spear-Phishing and Phishing Attacks
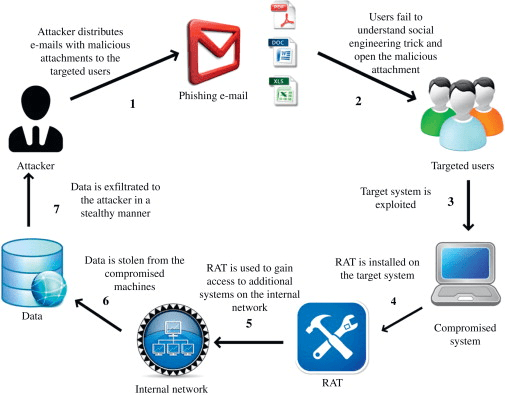
Image Source: ScienceDirect
A phishing attack is a way of transferring emails that show to be from credible sources with the purpose to expand personal data or guide folks to do something. It consolidates technical trickery and social engineering. It could include an attachment to a mail, which loads ransomware onto your machine.
Spear phishing is a targeted kind of phishing exercise. Attackers spend the time to carry research into targets and build texts that are private and appropriate. Due to this, the attack can be quite tough to recognize and even more complex to protect against.
One of the easiest methods to carry out this attack is email spoofing. It occurs when the data in the “From” segment of the email is forged, making it occur as if it is originating from someone you recognize, including your partner company or management.
4. Password Attack
Since passwords are the most generally utilized mechanism to validate users to a data system, gaining passwords is a natural and efficient attack method. It is possible to access an individual’s password by searching around the desk of the person, “sniffing” the link to the system
Access to a person’s password can be obtained by looking around the person’s desk, ‘‘sniffing’’ the connection to the system to get unencrypted passwords, obtaining access to password data, utilizing social engineering, or outright opinion.
5. Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Attack
Cross-Site Scripting attacks employ intermediary web resources to operate scripts in the web browser of the victim or scriptable app. Precisely, the attacker inserts a payload with malign JavaScript into the database of a website.
Defects that provide these attacks to work are considerably extensive and happen anywhere a web app utilizes information from a user in the output it creates without confirming or encoding it.
6. Malware Attack
It is described as an undesired tool, which is downloaded into your device without your permission. It can connect itself to genuine code and create lurk in helpful apps or gets copied all over the Internet. Here are a few of the most frequent sorts of malware:
- Macro Viruses: These viruses contaminate apps, including Microsoft Excel or Word. Macro viruses add to an app’s initialization string. When the app is used, the virus performs directions before carrying power to the app. The virus copies itself and connects to different codes in the system.
- Stealth Viruses: They control the system operations to hide. Stealth viruses do this by settling the malware detection tool so that the app will notify an infected region as being uninfected.
- Trojans: A Trojan horse or a Trojan is a program, which conceals in a helpful program and generally has a malign function. One of the core differences between Trojans and viruses is that the former ones do not replicate.
- Worms: Worms vary from viruses since they don’t connect to a host data file; however, self-contained applications that originate across computers and networks. Worms are usually diffuse via email attachments; accessing the email attachment stimulates the worm program.
- Ransomware: Ransomware is a kind of malware that bars access to the data of the victim and frightens them to delete or publish it except a ransom is given.
How to Prevent Your Data from Cyber Attacks?
“As cybersecurity leaders, we have to create our message of influence because security is a culture and you need the business to take place and be part of that security culture.”- Britney Hommertzheim
1. Back-Up Your Data
Back up your website and business data. It can assist you in recovering any data you miss if you encounter a cyber event or you have mechanical problems. Luckily, backing up does not commonly value much and is simple to do.
It is a great idea to utilize various back-up techniques to help guarantee the security of your valuable files. A stable back up method typically includes:
- Annual server back-ups
- Quarterly server back-ups
- Weekly server back-ups
- Daily incremental back-ups to cloud storage or a portable device
2. Secure Your Devices and Network
Make sure you draft your security software and OS to update automatically. Updates might receive critical safety upgrades for modern attacks and viruses.
Most updates let you schedule these updates subsequent to business hours or the others in a more suitable time. Updates fix severe safety defects, so it is essential to never neglect update prompts.
- Install Security Tool: Ensure the software consists of anti-spam filters, anti-spyware, and anti-virus.
- Set Up a Firewall: Setting up a firewall defends the internal networks of your business, but they need to be constantly patched to do their job.
- Turn On the Spam Filters: Utilize spam filters to decrease the volume of phishing and spam emails that your company receives.
3. Get a Proper Firewall on Your System
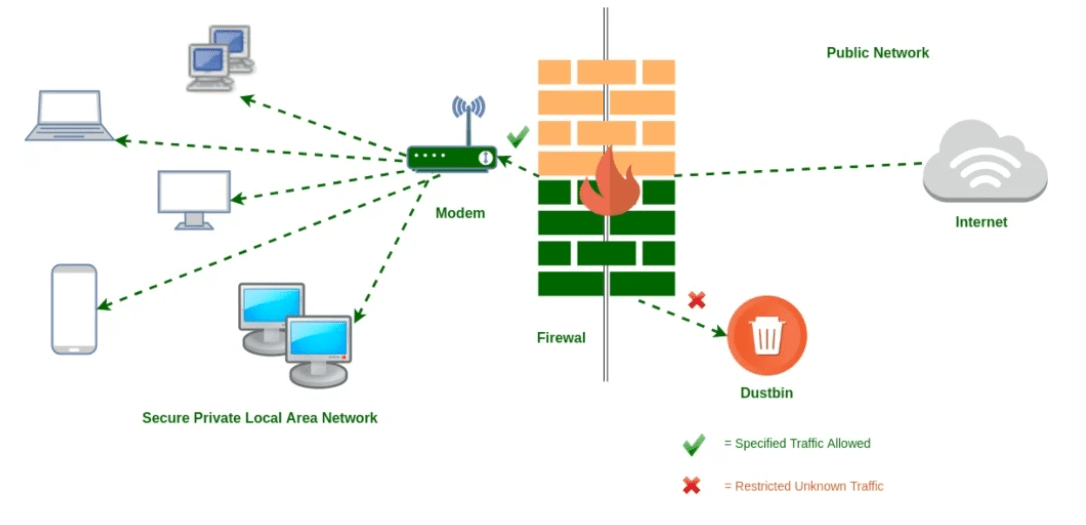
Image Source: GeeksforGeek
Your first line of protection is your firewall and plays a crucial role when an attacker attempts to enter your payment terminal. A firewall is a safety net that not only observes but even regulates incoming as well as outgoing system traffic based on proposed safety protocols.
A firewall can effortlessly discover if any information is being thieved from your network. It shuts down the process automatically if the firewall detects something mysterious occurring on your machine.
4. Encrypt Crucial Data
Ensure you switch your system encryption on and encrypt information whenever you share it. This changes your data into a mystery code before you share it across the internet. It lessens the danger of theft, tampering, or destruction.
5. Make Sure You Utilize 2FA (Two-Factor Authentication)
2FA is a two-step confirmation security method you need to give before you can use your account. You utilize two distinct validation aspects to confirm who you are, including your password, as well as a code sent to your mobile or your fingerprint.
The 2FA process adds an extra layer of protection, making it more difficult for hackers to get access to your online accounts or device.
6. Manage Passwords
Utilize strong passwords to guard access to your machines that contain vital business data. Owning a password, including ‘123456’ or adverser still, ‘password’ is quitting yourself exposed to being hacked.
In case you utilize a similar password for everything, as well as someone gets a grasp of it, your every account will get into danger. Thinking of using a password administrator that securely saves and generates passwords for you.
7. Regulate the Use of Computer Systems and Equipment
Maintain a record of different software equipment and tools that your company uses. Ensure they are safe to avoid forbidden access. Prompt your workforce to be cautious about:
- How and where they hold their devices?
- Utilizing USB portable or sticks hard drives. There could be an inadvertent transfer of unknown or other dangerous viruses from home to your company.
Eliminate any equipment or tool that is not required, ensuring that they don’t hold delicate data. If unused or older tools stay part of your organization’s network, it is uncertain they are going to be updated and perhaps a backdoor aimed by offenders to strike your business.
8. Establish Policies to Supervise Your Staff
A cybersecurity policy assists your staff in understanding their duties and what is adequate when they share or use:
- Emails
- Data
- Internet sites
- Computer and devices
Besides, it is crucial to have a robust social media system. This perhaps sets out what sorts of business data your staff can distribute online and where. A hacker could tailor persuasive data they post online.
Make sure your workforce is familiar with the policies and evaluate them frequently.
Final Thoughts
Undoubtedly, cybercrimes have escalated rapidly within the last few years. Not only enterprises but even governments are struggling to protect their data. According to experts, this trend is predicted to remain in 2021 and beyond with a few estimates showing that there are around 1M unfilled positions globally.
So, does cyber attack only affect your revenue?
The answer is No!
Corporations that have become the victims of cybercrimes not only suffered from economic loss but even faced user trust and loyalty problems.
Thus, no matter what the size of your business is, defending the information of your customers should be your priority.
Considering the given scenario, I have revealed some of the reliable practices to protect your business from cyber-attacks.
Always ensure that you always backup your data! Losing your data can be the worst nightmare. So, be ready and active against cybercrime.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is Cybersecurity?
A1: Cybersecurity is the body of practices, processes, and technologies developed to protect devices, data, networks, and devices from damage, attack, or unvalidated access.
Q2: Why is Cybersecurity crucial?
A2: Cybersecurity is essential since it incorporates everything that concerns preserving your delicate data, PII (Personally Identifiable Information), PHI (Protected Health Information), data, personal information, intellectual property, and industry and governmental information devices from theft and damage attempted.
Q3: What are the Top 10 Cybersecurity Threats?
A3: Following are the cybersecurity threats:
- Ransomware.
- Social Engineering.
- Patch Management.
- Third-Party Exposure.
- Cloud Vulnerabilities.
- Mistaking Compliance for Protection.
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Outdated Hardware
- Mobile Security Threats.
- Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) Policies.
Q4: What are the Benefits of Cyber Security?
A4: Here some advantages of cybersecurity:
- It protects end-users.
- Increase recovery time after a data breach.
- It protects your business against malware, phishing, ransomware, and social engineering.
- Cybersecurity avoids unauthorized users.
Q5. What are Cyber Security Standards?
A5: Cybersecurity standards are methods usually outlined in issued materials that try to preserve the cyber ecosystem of a user or company.
Q6. What are the Five Key Principles of Cyber Security?
A6: Below is the 5 principles of cybersecurity:
- Notice/Awareness
- Choice/Consent
- Integrity/Security
- Access/Participation
- Enforcement/Redress.
Q7. What are the Best Enterprise Cybersecurity Software?
A7: Following are the top enterprise cybersecurity tools:
- SolarWinds Security Event Manager
- Intruder
- Bitdefender Total Security
- Malwarebytes
- Mimecast
- CIS
- Snort
- Wireshark
- Webroot
